Digital Insights #68
Industry 5.0: Part 3 of 4
Ken Forster
Industry 5.0 - Beyond Principles - Evolving More Beneficial Outcomes
In our last installment, we highlighted the core tenets of Human-Centricity, Resilience, and Sustainability. The EU articulates a vision that will move past a narrow, traditional focus on technology or economic enabled growth to a more transformative concept.

Growth objectives incorporate elements of human, societal progress, and well-being. Industry 5.0 can be rightly seen as an evolution, incorporating foundational elements of Industry 4.0 into a more broadly encompassing vision that delivers a wider range of benefits to a broader set of stakeholders.
The goal is to move past economic and resource extractive models to new forms of sustainable, circular value creation that allow for a broader and fairer distribution of economic prosperity. This vision builds upon the foundations of the Industry 4.0 focus on hyper-efficient, technology optimized production systems to a broader mission guided by principles of regenerative purpose and transformation of industrial production to deliver broader value to society and the environment rather than a singular focus on shareholder value. The table below outlines key distinctions.
Evolving and Complementary Models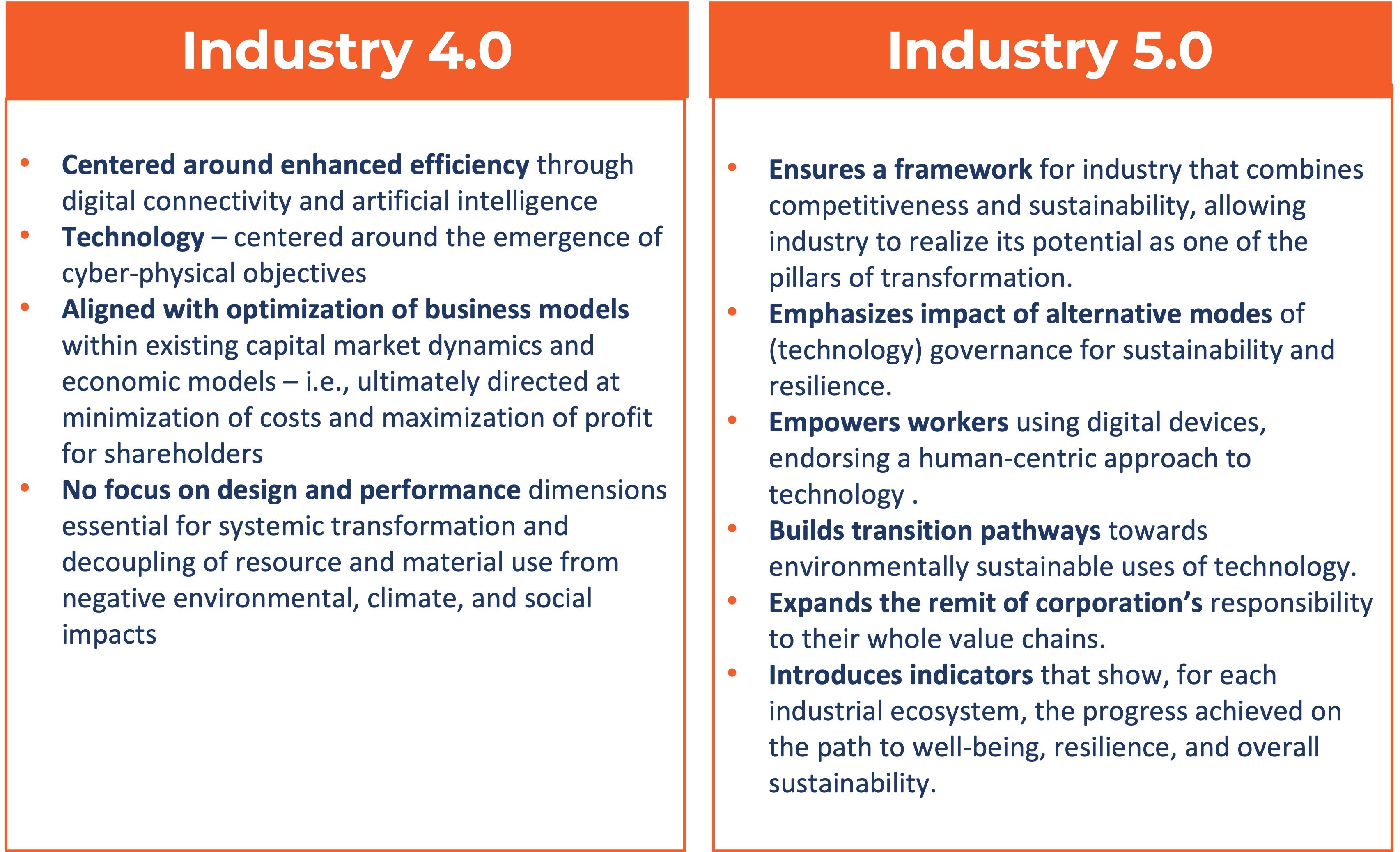
Building on Foundations
The European Commission defines six categories of technology expected to provide catalysts for Industry 5.0. The first three categories are already fully embedded into the current Industry 4.0 paradigms.
1.
Digital twins and simulation. The more forward-looking firms in discrete manufacturing and industrial design are already embracing these technologies, driving new standards of quality, efficiency, and anticipatory visibility into their products and ecosystems.
2.
Data transmission, storage, and analysis technologies. The fuel that powers innovative industry is data. The massive advances in connectivity, storage and data analytics, including cloud and edge-based systems, are foundational not just to industry but to every type of organizational venture across the globe.
3.
Artificial Intelligence (AI). Machine learning and AI technologies drive quantum acceleration in innovations, quality, and production, becoming an essential toolkit for all manufacturers.
The next three categories overlay the broader Industry 5.0 principles into more broad-reaching applications.
4.
Individualized Human-machine interaction. This is perhaps the most important distinction of Industry 5.0 – re-introducing the human element into processes and systems that have been automated to hyper-efficiency through information technologies. In one sense, the human element brings the soul back to manufacturing by enabling collaborative production – the imagination and flexibility of the human worker becomes empowered and advanced with the ability to harness collaborative robots (or co-bots). The combination of smart machines and savvy humans will allow for true “mass personalization” and more nimble production.
5.
Bio-inspired technologies and smart materials. There is no greater model of efficiency and sustainability than nature. Producers face limits of purely industrialized processes – particularly the extractive nature of certain industries, wasteful use of resources, and negative environmental impact remain challenges. Innovations in lighter, stronger, and more flexible materials, with an increased eye on being bio-friendly, promise a new generation of better products – for companies, customers, and the planet.
6.
Technologies for energy efficiency, renewables, storage, and autonomy. The transition from fossil fuel-powered transportation to Electric Vehicles is accelerating. At the same time, wind and solar power adoption continue to grow due to the declining cost curves and economies of scale in battery production. Advances in autonomous technologies promise to enable new business models for transportation while improving safety and reducing pollution.
Leading to Balanced Outcomes
Realizing the updated vision for Industry 5.0 will require new economic priorities to measure industry performance, new structure and design of business models, value chains and supply chains, updated objectives for digital transformation, innovative approaches to policymaking that better align the interests with business and industry, new ways to drive innovation and research capabilities, while better aligning the interests of businesses with broader society, government, and environment. The lessons learned from the pandemic underscore the compelling need to build resilience across value chains while securing jobs and economic security.
In our next segment, we look at where Industry 5.0 could lead and what businesses will need to do to prepare.
Reach out to me via LinkedIn if you would like to discuss this topic further.

Momenta is the leading Digital Industry venture capital + growth firm accelerating deep-tech innovators across energy, manufacturing, smart spaces, and supply chain. Our team of deep industry operators has helped scale industry leaders and innovators via our award-winning executive search and strategic advisory teams for nearly a decade.
Schedule a free consultation to learn more about our Digital Industry practice.



