Digital Insights #66
Industry 5.0: Revolutionary and Evolutionary Part 2 of 4
Ken Forster
Industry 5.0 - Both Revolutionary and Evolutionary
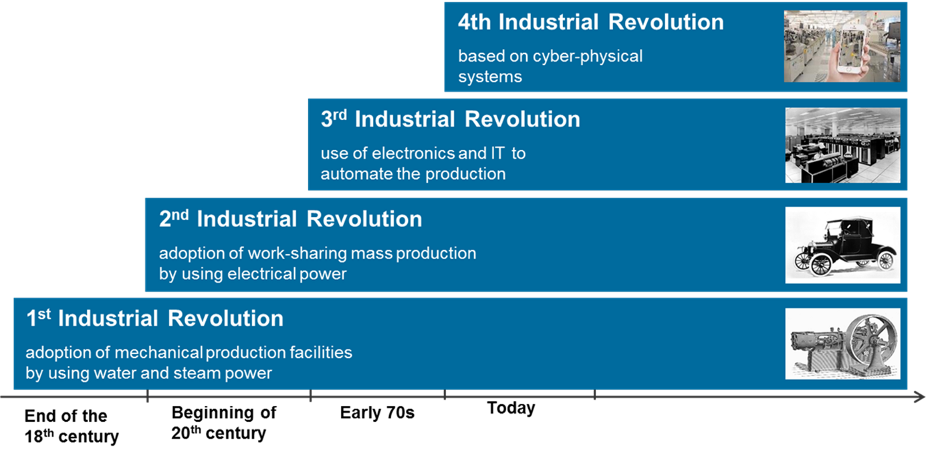
The vision of Industry 4.0 has primarily focused on creating optimized value chains through the application of advanced technologies. To put this in historical perspective, Industry 4.0 was conceived as the realization of the Fourth Industrial Revolution.

The First Industrial Revolution dates back to the 1780s, with the innovations around generating power from water, steam, and fossil fuels. The Second Industrial Revolution emerged in the 1870s with the introduction of electrical energy, which allowed for the development of assembly lines and mass production. The Third Industrial Revolution emerged in the 1970s with the rise of Information Technologies and semiconductors, enabling unprecedented automation across industries. The Fourth Industrial Revolution incorporates the components of Internet of Things (sensors, low power connectivity, etc.) with cloud computing and advanced analytics to create real-time interactions between virtual and physical environments – giving rise to cyber-physical systems.
Source: https://medium.com/@marcellvollmer/what-is-industry-5-0-a363041a6f0a
Industry 4.0 originated from a German government strategy project focused on transforming manufacturing into cyber-physical systems that generate significant savings in costs of production, logistics, and improved quality management. The essential approach involves deploying IoT technologies in manufacturing facilities, collecting, and analyzing the data using cloud computing, the using big data insights to power more efficient value chains. Effectively, Industry 4.0 is about automating processes and incorporating edge computing (both sensors and actuators) – the pure application of technology to create smart factories, leverage digital twins, and realize hyper-optimized production lines and smart products.
While Industry 4.0 is still in the initial stages of evolution, industry leaders have been looking ahead to the concept of a Fifth Industrial revolution that incorporates the principles of human-centricity, sustainability, and resilience.
Incorporating the Human Element
One of the core tenets of Industry 5.0 is to make processes more human-centric. Part of the motivation is to mitigate the concerns and resistance to automation from labor unions and politicians concerned that Industry 4.0, in theory, could create crises of technological unemployment. From a practical perspective, highly automated processes can deliver highly consistent and repeatable output, but this does not address the need to provide increasingly customized or personalized products (as customer expectations become increasingly sophisticated).
The human-centric vision involves active collaboration between people and machines. Historically automation and robotics have tended to be isolated from humans on the factory floor (often behind cages for safety reasons). A new generation of collaborative robots (also known as cobots) incorporates enhanced sensor and vision technologies to enable humans to work alongside cobots. In addition to being inherently safer, the new generation of cobots is easier to program and set up. It can be “trained” to work alongside humans on the factory floor and can be reprogrammed to perform a wider range of tasks as needed. The vision of Industry 5.0 is to harness the creativity of humans in a far more extensible framework to deliver a more dynamic range of manufactured products.
Sustainability as Core Principle
There has been a significant focus on sustainability coming from the EU, figuring prominently in policy. The EU has been fully committed to delivering on the UN’s 17 Sustainable Development Goals, including adopting more green energy, reducing environmental impact, and promoting social goals such as the empowerment of women, particularly in developing countries. Sustainability is an increasing corporate priority, combined with the growing investor focus on ESG factors guiding investment decisions.
The Industry 5.0 vision seeks to offset the typical increases in energy consumption and carbon emissions from the expansion of industrial production. Improvements can come from increased energy efficiency, sourcing of clean power sources, focusing on reducing pollutants and their environmental impact, and using new materials. The concept of “circular economy” in which materials and waste products are recycled to minimize any negative impact on the environment figures prominently, though this will require significant research and innovation ahead.
Making Industry and Society More Resilient
There has been no more dramatic illustration of the need for resilience than the severe supply chain and employment disruptions created by the pandemic and responses. Manufacturers have had to re-evaluate their supply chains and the reliability of vendors. In many regards, ensuring resilience can be at odds with the hyper-efficient model of “just-in-time” principles – but in times of disruption, the downside of reliance on global suppliers (and static processes) can be far more costly.
The other dimension of resilience is societal – again, the potential downsides of widespread technological unemployment created by hyper-efficient automation can result in heightened – and potentially dangerous social instability. The incorporation of the human element and sustainable principles into manufacturing processes promises improved resilience on multiple counts.
The human-centric, sustainable, and resilient principles of Industry 5.0 address a broader range of considerations than the pure technologically driven efficiencies envisioned by Industry 4.0.
Next, we will explore some of the benefits and outcomes of Industry 5.0 – and the road ahead. Stay tuned.
Reach out to me via LinkedIn if you like to discuss this topic further.

Momenta is the leading Digital Industry venture capital firm accelerating deep-tech innovators across energy, manufacturing, smart spaces, and supply chain. Our team of deep industry operators has helped scale industry leaders and innovators via our award-winning executive search and strategic advisory teams for nearly a decade.
Schedule a free consultation to learn more about our Digital Industry practice.



