Momenta's Take: Value Reality - The state of VR in Industry
Ed Maguire

Unlocking the Potential: Assessing VR's Impact on Industry
One of the most heavily hyped technologies over the past decade has been Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR), with tech giant Facebook rebranding itself Meta to emphasize focus on the Metaverse (a virtual environment accessible to users of VR devices such as the company’s Oculus). While the immersive nature of VR is revolutionary, adoption initially failed to meet elevated expectations, and use cases beyond gaming have failed to catch on for VR.
In contrast, Augmented Reality technology, which overlays digital information overviews of the physical space, has seen many practical use cases adopted by industry. Beyond its military origins (such as digital visors for combat pilots), Industrial AR technology is firmly established, having been used to facilitate advanced training, remote service functions, inspection, and assisting manufacturing processes. Interest in the Metaverse has been slower to catch on outside of entertainment, but that appears to be changing. The most commonly referenced definition of the Metaverse comes from Matthew Ball: “an expansive network of persistent, real-time rendered 3D worlds and simulations that […] can be experienced synchronously by an effectively unlimited number of users, each with an individual sense of presence.” Strategist Ben Thompson argues that this description is similar to what the Internet does already, with a 3D layer on top of it.
The Industrial Metaverse – Vision Taking Shape
There is growing interest in the concept of Industrial Metaverse, which encompasses multiple technologies that, when used together, create an immersive 3D virtual or virtual/physical industrial environment that will ultimately be able to be accessed from any connected device, including VR/AR hardware, smartphones, computers, and equipment.
According to Forrester, the Industrial Metaverse does not yet exist, but its building blocks do, and when connected with physical systems, they can deliver value in asset-intensive industries.
Building Blocks of the Industrial Metaverse
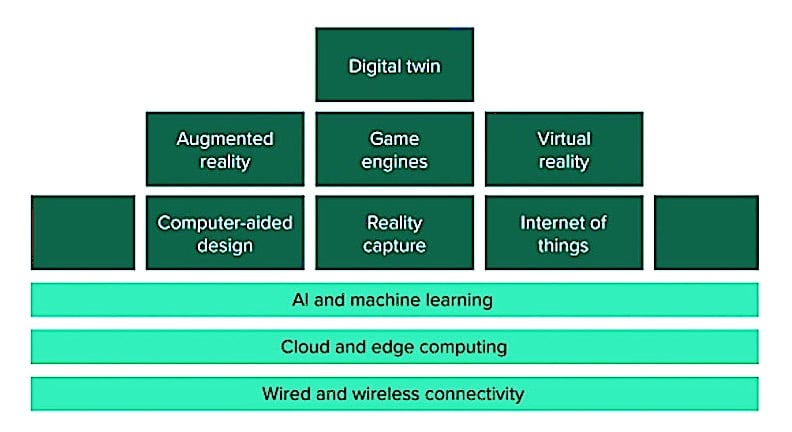
Source: Forrester
The challenge lies in integration; large firms commonly use systems from different vendors. Systems such as a motor or robot sold with a digital twin from a vendor such as ABB or Siemens do not necessarily work easily with systems from other vendors.
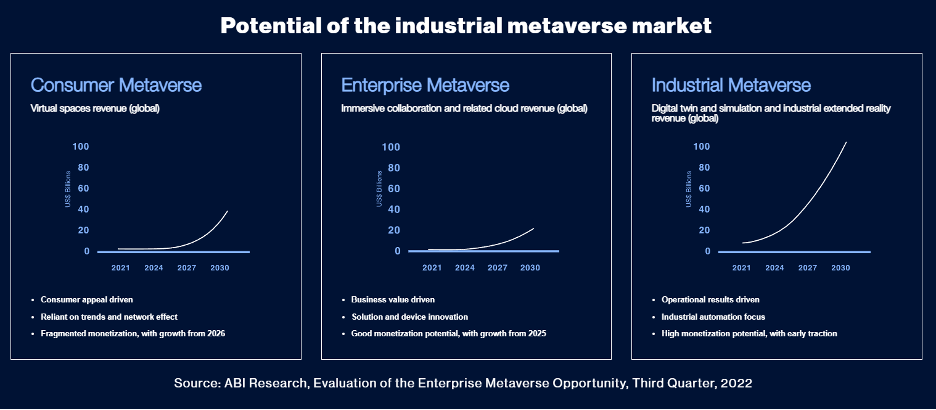
According to Thierry Klein of Bell Labs Solutions Research at Nokia, the Industrial Metaverse can reach “a much larger scale with increasing complexity by creating digital twins of entire systems such as factories, airports, cargo terminals, or cities—not just digital twins of individual machines or devices.” IDC predicts that by 2025, 20% of Global 2000 manufacturers will include the industrial Metaverse in their digital transformation roadmap to address advanced simulation, cross-domain collaboration, and safety. ABI Research forecasts that revenues for industrial digital twin and simulation and industrial extended Reality will reach $22.7 billion by 2025 as organizations use Industry 4.0 tools such as AI, machine learning, edge computing, and extended Reality to accelerate digital transformation.
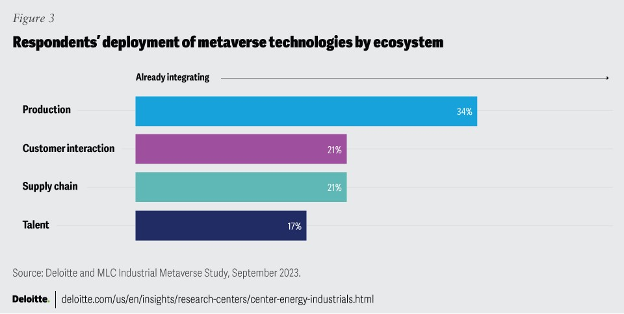
In May 2023, Deloitte and the Manufacturing Leadership Council surveyed 350 senior leaders at US manufacturing firms and found that 92% are already investing in technologies that could serve as the foundation for an industrial Metaverse. Building on smart factory efforts and leveraging foundational technologies in place, the most common use cases focus on the production ecosystem, with over 1/3 of respondents already integrating Metaverse technologies, followed by the customer, supply chain, and talent ecosystems.
In these early stages, the Industrial Metaverse exhibits similarities with Industrial IoT and the broader Internet landscape. While foundational technologies are advancing independently, the primary challenge lies in seamlessly integrating multiple systems to ensure a cohesive user experience. We firmly believe that organizations should prioritize the establishment of a long-term strategic and architectural framework for their Industrial Metaverse vision. This strategic approach ensures that investments in AI, CAD, Realty Capture, Digital Twins, and other essential components create feasible pathways for integration. Embracing this strategic blueprint for the Industrial Metaverse promises time and resource savings, ultimately leading to a substantial return on investment.

Momenta is the leading Industrial Impact venture capital + growth firm. We accelerate entrepreneurs and leaders devoted to the digitization of energy, manufacturing, smart spaces, and supply chains. Since 2012, our team of deep industry operators have invested in over 50 entrepreneurs and helped scale over 150 industry leaders via our award-winning executive search and strategic advisory practices.



